📅 2011, IPv4 Address Exhaustion Declared#
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), which manages internet addresses, declared that there would be no more IPv4 allocations. While IPv4 can use approximately 4.3 billion limited addresses, the rapid increase in internet demand exhausted the IPv4 addresses allocated to each continent.
But How Are We Still Using IPv4?#
So here we are in 2022, 11 years after IPv4 ran out, and we’re still using IPv4 just fine. How is this possible?
IPv6 was developed long ago and is gradually being commercialized. Nevertheless, IPv4 usage is still much more prevalent, so how has it been maintained well until now, 11 years later?
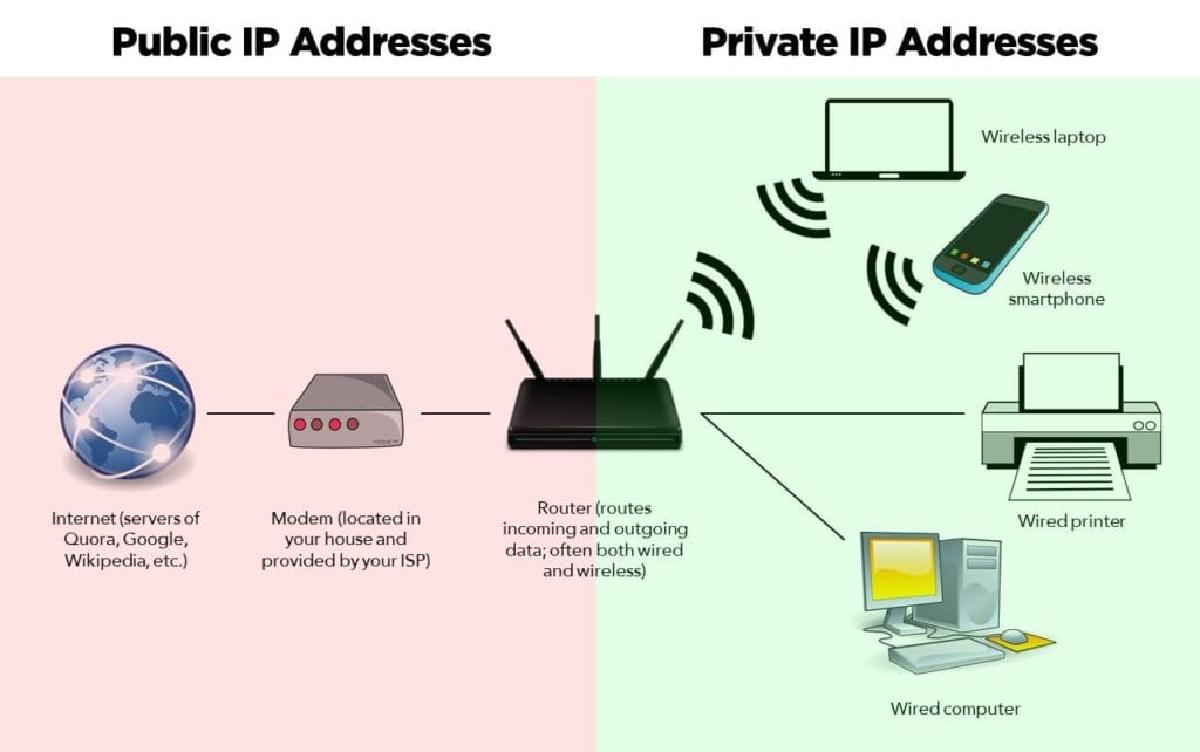
🔌 What is a Private Network?#
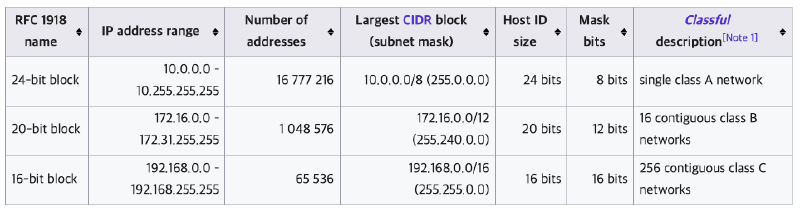
A private network refers to a network that uses a specific range of IPv4 addresses within limited spaces such as homes and businesses, rather than on the public internet. Private IP ranges that belong to private networks can only be used within the private network (internal network), so they cannot be used on the public network (external network, internet).
What is a Public IP?#
A public IP is necessary for different PCs to communicate with each other over the internet and is used for purposes such as:
- Building website servers
- PC internet connection
- Communication via the internet
💡 Concept Summary#
So how do we communicate with other PCs that don’t use the same private network as us?
We need a public IP!
In other words, special measures are needed to communicate with the public internet from a private network. Private IPs are regulated to be used only within private networks, so private IPs cannot be used on the public internet.
🔄 NAT (Network Address Translation)#
To address this, Network Address Translation (NAT) was devised as a method to convert IP addresses.
What is NAT?
It refers to a technology that sends and receives network traffic through a router while rewriting TCP/UDP port numbers and source and destination IP addresses of IP packets. Since changes occur in packets, IP and TCP/UDP checksums must also be recalculated and rewritten.
The reason for using NAT is usually to allow multiple hosts belonging to a private network to access the internet using a single public IP address.
In other words, it means converting to the IP used in the public/private network when communicating from a private network to a public network and vice versa. According to the above explanation, converting TCP/UDP port numbers of IP packets is actually because NAT includes not only IP addresses but also port conversion!
It’s called PAT or NAPT (Port Address Translation).
📡 Router Functions#
These days, most homes have routers installed and in use (e.g., iptime, olleh, etc.).
These routers have various functions.
1. DHCP Server Function#
First, there’s a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server function that assigns IPs to various devices connected through a single router.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
DHCP is an IP standard that simplifies host IP configuration management. It provides a method to dynamically assign IP addresses and other related configuration details to DHCP-enabled clients on the network using a DHCP server.
Through this, smart devices and PCs inside the house connected to the router are each assigned a private IP.
Why are they assigned private IPs?
If you go back to the very first explanation, you’ll understand…?!
Since the number of IP allocations is limited, we can’t assign a public IP to every home, or rather, every device, so we assign private IPs to build a private network! By building a private network this way, communication is possible internally, but we still can’t communicate with the external internet.
2. NAT Function#
That’s why routers have a NAT function.
- Function to convert private IPs to public IPs
- Build their own mapping table and manage pre-conversion and post-conversion values with a NAT table
What is a VPN (Virtual Private Network)?#
Going further, let’s learn about VPNs, which we may have used but don’t know exactly what role they play!
The VPN I knew was something that changes IPs or fakes IPs for illegal purposes… 🤔
I thought it was something like that, but it’s half right and half wrong!
The True Meaning of VPN#
VPN refers to being able to use an external computer as if it were connected to an internal network (private network).
The reason why the IP changes when using VPN can also be understood if you think carefully about private/public networks mentioned above.
💼 VPN Use Cases#
1. Remote Work/Telecommuting#
Through this, companies with private networks set up VPN servers, and through external public IP addresses and configured IDs/passwords, you can access the company’s private network from anywhere.
2. Remote Computer Access#
Similarly, for personal computers, through VPN setup, if you know the external public IP address, you can access your computer in Seoul from Jeju Island through VPN from anywhere.
3. Bypassing Geographical Restrictions#
When a website in a certain country blocks access from our country’s IP, we cannot access that site. To access this site, we need to approach with an IP address from a country other than ours. At this time, through VPN, we can bypass the blocked firewall as if we’re accessing from an internal network in another country.
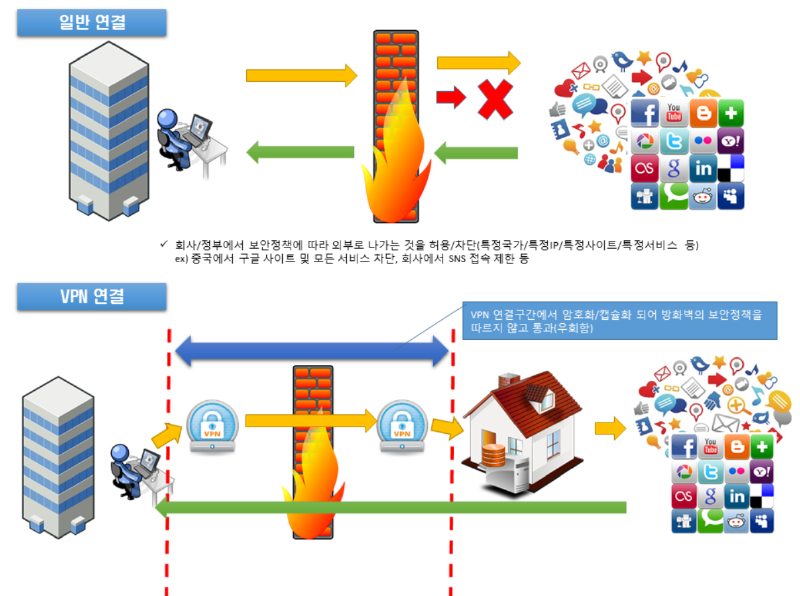
4. Firewall Bypass Mechanism#
Hypothetical Scenario
If a company blocks access to SNS during work hours as an internal policy, we connect through VPN set up at home or an overseas VPN. Then we can access SNS.
Why does this work?
The moment you connect to VPN, a virtual tunnel is formed, and packets sent for communication between tunnels are broken down into smaller pieces and undergo encryption and encapsulation. At this time, although it passes through the company’s firewall, because it’s an encrypted/encapsulated packet, the firewall cannot detect that you’re trying to access SNS through VPN, so it lets the packet pass through.
📋 VPN Summary#
👍 Advantages#
- Data security
- 🔒 Online privacy protection
- 📍 IP address change
- 🛡️ Personal protection
- 🚀 Bandwidth throttling prevention
👎 Disadvantages#
While VPN has many advantages as mentioned above, it also has disadvantages.
- 🐢 Devices connected to VPN must communicate with the VPN server using encryption, so network speed is very slow
- ⚠️ Some VPNs with low reliability exist
- 💰 You must pay to use VPNs with high security
- 🚫 Not available in some countries