What is Dispatcher Servlet?#
The term dispatch in Dispatcher Servlet means “to send”. The Dispatcher Servlet can be defined as a Front Controller that receives all incoming HTTP protocol requests first and delegates them to the appropriate controller.
Operation Overview#
The more detailed process is as follows:
- When a request comes from the client, a servlet container such as Tomcat receives the request
- All these requests are received first by the Dispatcher Servlet, which is the Front Controller
- The Dispatcher Servlet processes common tasks first and then finds the controller that should handle the request and delegates the work
Front Controller Pattern#
The term Front Controller refers to a controller that receives and processes all client requests coming to the server at the front of the servlet container, and it is a design pattern used together with the MVC architecture.
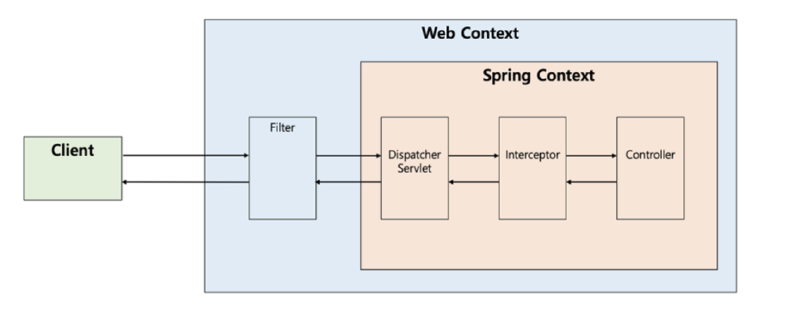
How Dispatcher Servlet Works#
The Dispatcher Servlet is the Front-Controller that receives requests first.
- It passes through filters in the Servlet Context (Web Context)
- The Dispatcher Servlet receives the request first in the Spring Context
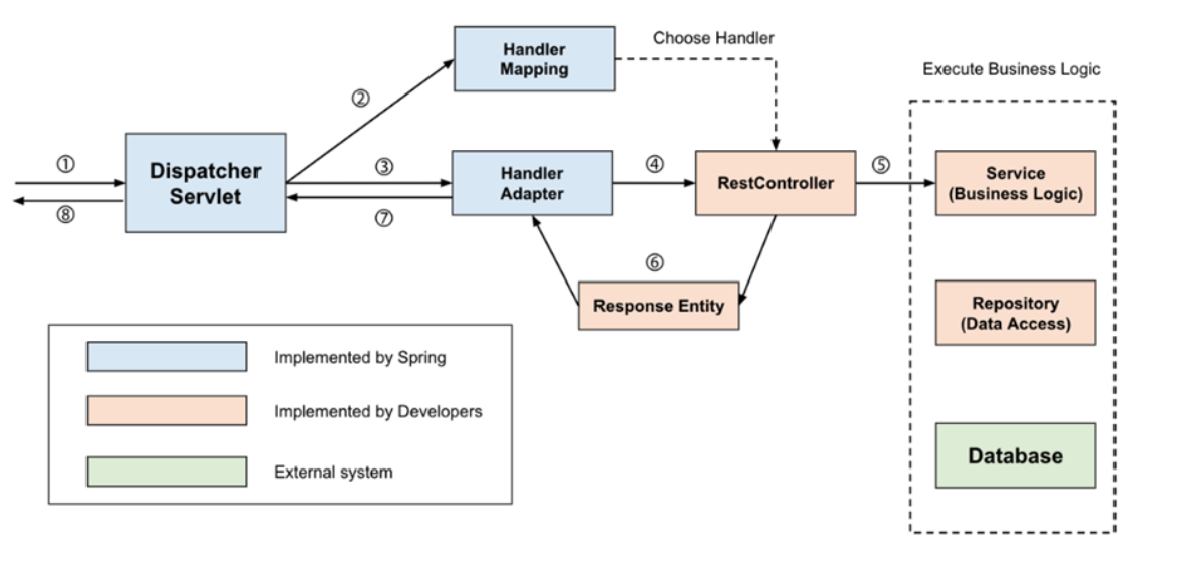
The Dispatcher Servlet must find the appropriate controller and method to delegate the request, and the operation process is as follows.
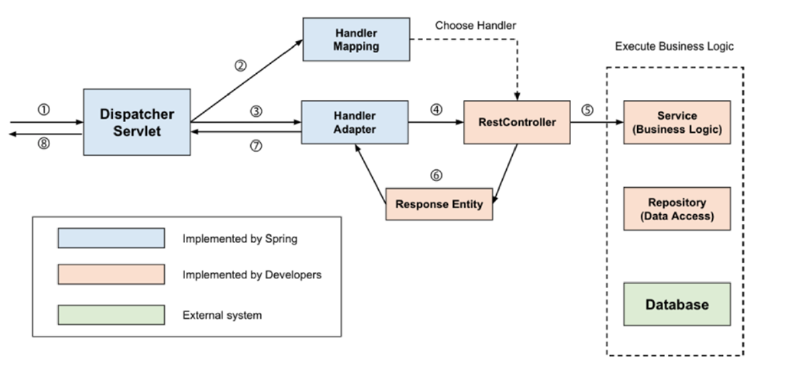
Detailed Operation Process#
1. HTTP Request passes through Filter and is received by Dispatcher Servlet#
2. Check request information and find the Controller to delegate#
RequestMappingHandlerMapping, one of the implementations of HandlerMapping, parses all controller beans written with @Controller and manages (request information, processing target) as a HashMap.
It finds the HandlerMethod object that contains the controller and method mapped to the request. Therefore, when a request comes in, HandlerMapping creates a Key object (request information) using HTTP Method, URI, etc., finds the HandlerMethod to process the request as Value, wraps it in HandlerMethodExecutionChain, and returns it.
The reason for this wrapping is to include interceptors that need to be processed before passing the request to the controller.
3. Find and pass the HandlerAdapter to delegate to the Controller#
The Dispatcher Servlet does not delegate requests directly to the controller, but delegates them through HandlerAdapter.
The reason for going through the HandlerAdapter interface is that there are various ways to implement controllers. While controller classes are mainly written using @Controller with @RequestMapping related annotations, controller classes can also be written by implementing the Controller interface.
Therefore, Spring applies the adapter pattern through the HandlerAdapter interface, allowing requests to be delegated to Controllers regardless of the controller implementation method.
4. HandlerAdapter delegates the request to the Controller#
Common pre/post processing is required before HandlerAdapter passes the request to the Controller.
Typically:
- Interceptor processing
- ArgumentResolver to handle
@RequestParam,@RequestBody, etc. in requests - ReturnValueHandler that handles processing such as serializing the Body of
ResponseEntityto JSON in responses
These processes are handled before being passed from the adapter to the controller. Then it delegates the request to invoke the controller’s method.
5. Process Business Logic#
The Controller calls the service and proceeds with business logic.
6. Controller returns the return value#
Returns ResponseEntity or View name.
7. HandlerAdapter processes the return value#
HandlerAdapter returns the response received from the controller to the Dispatcher Servlet after post-processing by the ReturnValueHandler, the response processor.
- If the controller returns
ResponseEntity→HttpEntityMethodProcessorusesMessageConverterto serialize the response object and set the response status (HttpStatus) - If View name is returned → View is returned through
ViewResolver
8. Send the server’s response to the client#
The response returned through DispatcherServlet passes through the Filter again and is returned to the client.